
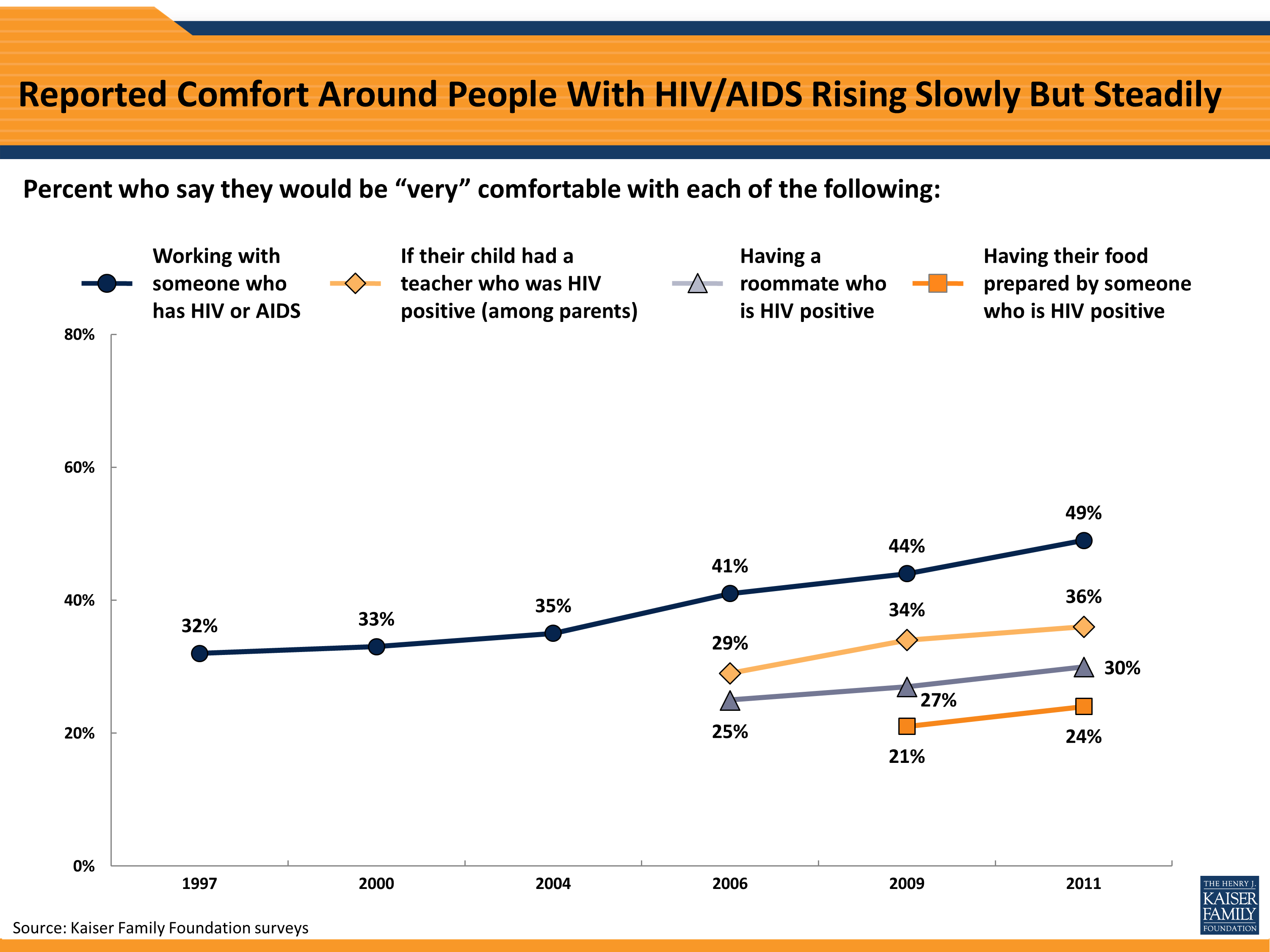
Using a condom or dental dam can further reduce the already low risk, as can taking medicine to prevent or treat HIV. Even then, it’s unlikely that a person will be infected by having oral sex.

These include coexisting sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and bleeding gums. Still, there are certain factors that may increase the potential for infection. The CDC says that the risk is hard to quantify, because a lot of people who have oral sex have anal or vaginal sex, too. While there is a possible risk of getting HIV from oral sex, the documented risk remains extremely low. “Identifying your personal risk, therefore, allows you to take the steps needed to protect yourself and others.” 4. “The simple truth is that people can and do get infected after a single exposure,” says Dr. The more you engage in these activities, the more likely you are to contract the virus. Insertive penile-vaginal sex: 1 in 2,500.
Receptive penile-vaginal sex: 1 in 1,250.Here is the estimated probability of acquiring HIV from an infected source, per exposure act, according to the CDC: Of these, unprotected anal sex poses the highest risk. The three main routes of HIV infection in the United States are anal sex, vaginal sex, and shared needles. Which Activities Are Most Likely to Transmit HIV? “Just because a person comes into contact with tiny quantities of HIV in blood or semen doesn’t mean that an infection will occur,” says Dennis Sifris, a physician and HIV specialist with the Lifesense Disease Management Group in Johannesburg, South Africa. Even in a healthcare setting, the risk of infection from a needlestick injury is only around 0.3 percent. For example, there have been no confirmed cases of HIV caused by a blood-tainted needle in a public place to date. Compared with other types of viruses, such as influenza or chicken pox, HIV is relatively fragile: It does not thrive at room temperature (68 degrees F), when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, or at pH levels that are dissimilar to that of blood.Įven if a small amount of virus does manage to survive for a short period of time, the odds that it will infect you are next to zero. Without these defenses, a person will be at high risk for serious illnesses that a healthy person would be able to fight off.ĪIDS is diagnosed when a person has a CD4 count of less than 200 (meaning less than 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood) or has at least one of 27 AIDS-defining conditions outlined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), such as recurrent pneumonia and some lymphomas. These infections, which are called “opportunistic,” tend to be mild in the early stages and can become progressively worse as the immune system is depleted.ĪIDS, or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, is the stage of the disease when the immune system is weakened by the loss of CD4 cells (also called T-helper or T-4 cells) - white blood cells that help fend off harmful pathogens in the body. Specifically, HIV, or the human immunodeficiency virus, is an infectious virus that gradually breaks down a person’s immune system, leaving the body less able to defend itself against viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. HIV is a virus, while AIDS is a stage of advanced infection. Here, then, are some myth-busting answers to the most commonly asked questions about HIV. Unfortunately, false assumptions can increase the risk of infection and the odds of transmitting the virus to someone else. Although people know a lot more about HIV than they used to, there are still plenty of misconceptions about the virus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
